Managing challenging behaviour in adults can be tough, but understanding its causes makes a big difference.
In this post, we’ll dive into 4 reasons for challenging behaviour and share practical tips for caregivers and professionals. Addressing these causes can create a more supportive and positive environment for everyone.
Table of Contents
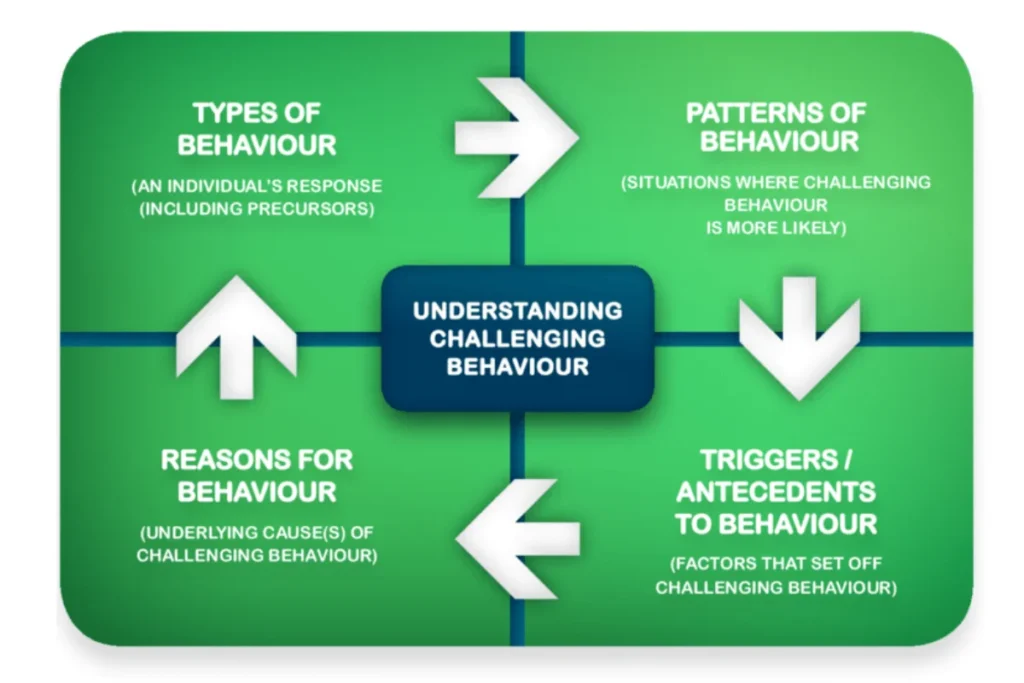
What is Challenging Behaviour?
Challenging behaviour refers to actions or reactions that interfere with an individual’s daily activities or affect others around them. These behaviours can be difficult for both the individual and caregivers. They may cause emotional, social, or physical challenges for everyone involved.
These behaviours usually stem from unmet needs, frustration, or difficulty expressing feelings. Understanding challenging behaviour in care helps caregivers offer the right support. By spotting the signs and recognising the triggers, caregivers can create a supportive environment that addresses the individual’s needs.
If your situation needs further considerations, you may want to consider what is required when selecting a care home. We have a guide that can provide more information on how to choose a care home in the UK.
Common Types of Challenging Behaviour
- Aggression towards others
- Self-harm or self-injury
- Verbal outbursts or shouting
- Withdrawal or refusal to engage
Because these behaviours are unique to each person, it’s important to understand care home options. Our blog about types of care homes in the UK can help you find the best fit.

4 Common Reasons for Challenging Behaviour in Adults
We must describe possible reasons for behaviour that challenge us because they are rarely simple. These behaviours often result from a combination of a person’s inner feelings and their environment.
Let’s investigate four primary factors that can cause these behaviours. Keep in mind that these actions are often rooted in an underlying need or some form of distress.
Reason 1: Communication Difficulties
Many individuals who exhibit challenging behaviours struggle with communication. Frustration due to the inability to express needs and feelings can manifest as disruptive or harmful actions.
- Limited language skills make it hard to express needs, leading to frustration and challenging behaviours.
- Those with speech impairments or learning disabilities often resort to challenging behaviours when they cannot communicate their thoughts or desires effectively.
- A lack of understanding between the individual and their caregivers exacerbates the issue, creating misinterpretations and further frustration.
How to Address It:
- Provide support through alternative communication methods: this includes sign language, speech therapy, and the use of communication boards. These methods empower individuals to express themselves.
- Be patient and offer frequent reassurance during communication attempts. Building trust is a key component.
Reason 2: Sensory Overload
Sensory sensitivities and processing differences are common in people who struggle with their behaviour. Being exposed to environments that are too overstimulating can cause immense distress and lead to challenging behaviours.
- Overstimulating environments, such as those with bright lights, loud sounds, or strong smells, can quickly overwhelm individuals and lead to distress.
- Sensory overload may manifest in physical outbursts, such as hitting or rocking, or withdrawal and shutting down.
- Sensory sensitivities are particularly common in those with autism or sensory processing disorders.
How to Address It:
- Use calming techniques when an individual appears to be overloaded. Dimming lights, and providing noise-cancelling headphones or weighted blankets can be beneficial.
- Create sensory-friendly spaces where the individual can retreat to relax and regulate their senses.
- Managing anger in autistic adults can be a real challenge. To learn how to handle this, check out our article on how to deal with autism anger in adults.
Reason 3: Emotional Triggers
Emotional triggers are often the root cause of behavioural disruptions, as individuals may struggle to manage overwhelming feelings.
- Anxiety or fear often manifests in physical outbursts, avoidance, or even self-harm.
- Unresolved trauma can trigger unexpected emotional responses, sometimes leading to aggression or withdrawal.
- Frustration from unmet emotional needs can also lead to the manifestation of negative behaviours.
How to Address It:
- Introduce calming routines to help reduce anxiety. This could involve regular breaks or quiet time.
- Provide emotional support through therapy or counselling. Professional help can address the root of the trauma or anxiety.
- Practice mindfulness techniques to help individuals regulate their emotions and become more self-aware.
Reason 4: Unmet Physical/Social Needs
When fundamental physical or social needs are not met, it can easily lead to challenging behaviour.
- Hunger, pain, or illness can manifest as aggression, irritability, or withdrawal from interaction.
- Loneliness and social isolation often lead to disruptive behaviours, such as attention-seeking actions or withdrawal.
- Unmet needs for comfort or personal care can trigger frustration and potentially, lead to acting out.
How to Address It:
- Guarantee proper healthcare with regular checkups and timely treatment for any physical discomfort.
- Create a social environment that encourages regular interaction to prevent isolation.
- Pay close attention to personal comfort and care needs, assuring they are met proactively.
How to Identify Challenging Behaviour and Its Triggers
| Step | Description | How to Implement |
| Observing Patterns | Caregivers need to monitor when and where the behaviour occurs to identify triggers. Understanding what comes before the behaviour can reveal patterns and potential links to specific situations. | 1. Keep a behavioural log to track patterns over time. 2. Record the specific behaviours, context, and any preceding events to identify triggers. |
| Professional Assessment and Support | When needed, it is crucial to seek professional help from psychologists, occupational therapists, or other specialists. A proper assessment can provide valuable insights into the underlying causes and help caregivers better manage challenging behaviours. | 1. Seek help from psychologists, occupational therapists, or other specialists for a thorough assessment. 2. Use the insights to create individualised support plans. |
Effective Solutions for Managing Challenging Behaviour
Addressing challenging behaviour involves implementing strategies that create a supportive environment, encourage positive actions, and improve communication. Below are practical approaches to manage such behaviours effectively:
Structured Routines:
- Consistent schedules reduce confusion and anxiety, particularly for those with autism or cognitive differences.
- Use a daily schedule with set times for meals, activities, and rest.
- Visual schedules (e.g. picture lists or calendars) help individuals understand what’s coming next and reduce worry, especially when changes are communicated in advance.
Positive Reinforcement:
- Rewarding positive behaviour encourages repetition and supports learning.
- Provide immediate, specific praise (e.g. “I like how calmly you asked for help”).
- Use reward systems like token charts, where tokens can be exchanged for desired items or privileges.
Calming Techniques:
- Teach deep breathing exercises to lower stress levels.
- Offer sensory tools like stress balls, weighted blankets, or quiet spaces to aid in self-regulation.
Effective Communication:
- Use simple, direct language and break tasks into smaller steps for clarity.
- Practice active listening and rephrase what the individual says to show understanding and build trust.
Positive Behavior Support (PBS):
- Conduct assessments to observe behaviours and identify triggers.
- Develop and regularly review customised support plans based on assessments, making sure they meet the individual’s needs.
It’s good to know who can access care homes in the UK when handling challenging behaviour. These homes offer support and structure for people who need help with everyday tasks. Learn about eligibility in our guide on who qualifies for care homes in the UK.
Preventive Strategies for Managing Challenging Behaviour
Managing challenging behaviour effectively requires proactive approaches to prevent escalation. Below are several strategies for dealing with challenging behaviour to help caregivers and professionals reduce the frequency and intensity of difficult behaviours.
| Strategy | Description | How to Implement |
| Early Intervention Techniques | Identifying early signs of distress and addressing them before they escalate is key to managing challenging behaviours. This approach helps prevent behaviours from intensifying. | 1. Observe for early signs of discomfort or frustration. 2. Implement calming techniques like deep breathing or providing breaks. 3. Adjust the environment if needed. |
| Positive Reinforcement | Rewarding positive behaviours to encourage their repetition. This technique helps individuals understand the benefits of engaging in desirable actions and discourages challenging behaviours. | 1. Use verbal praise or small rewards when an individual displays positive behaviour. 2. Create clear and consistent reinforcement strategies. |
| Structured Routines | A predictable, structured environment provides stability and reduces anxiety, helping individuals with challenging behaviours feel more secure. | 1. Develop and maintain consistent routines for daily activities. 3. Provide visual schedules or reminders to help individuals feel prepared for transitions. |
| Providing Comfort and Support | Offering comfort items or social support can alleviate discomfort and reduce the likelihood of challenging behaviours. Comfort items help individuals manage distress. | 1. Keep easy access to comfort items like soft toys, blankets, or sensory-friendly tools. 2. Develop social connections by encouraging interaction with trusted caregivers. |
Conclusion
Understanding the 4 reasons for challenging behaviour is key to offering better care. We’ve looked at the main causes and solutions that could help. As every person’s needs are unique, the support must be adapted to fit.
If you or someone you know needs assistance, get in touch with Metro Care UK. We’re here to offer guidance and support for managing challenging behaviour in more complicated situations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What can be the reasons for challenging behaviour?
Challenging behaviour often arises from unmet needs, like communication difficulties, sensory overload, or emotional distress. Physical discomfort, loneliness, and lack of social interaction can also contribute. These behaviours may signal frustration or an inability to cope with their environment.
What are the five steps to help you deal with challenging behaviour?
First, identify the trigger. Second, stay calm. Third, listen actively. Fourth, try gentle redirection. Fifth, consider environmental changes or professional help if the behaviours continue. Consistency and understanding are key to the process.
How do you identify challenging behaviour?
You can identify challenging behaviour by observing actions that disrupt daily life or harm the individual or others. This includes aggression, self-injury, shouting, or withdrawal. Look for patterns and triggers that precede these actions, to try to understand them better.
What is challenging behaviour in the NHS?
Challenging behaviour, as defined by the NHS, includes actions that risk the well-being of the individual or those around them. This can be in response to various causes including unmet health or social care needs. They require carefully constructed care and support plans.